TP6
Analysis of the pathobiology of dermatological abnormalities in patients with RASopathies
Germline and mosaic mutations in HRAS cause Costello syndrome, a RASopathy with significant epidermal manifestations, or congenital cutaneous disorders, respectively. We found that HRAS-RIN1 signaling dominates in epidermal keratinocytes and Costello syndrome-associated HRAS mutants affect vesicle-based trafficking of integrins via RIN1; thus, we identified a novel pathophysiologic quality for a RASopathy. To achieve our aims (see major goals), we will use heterologous cell lines expressing mutant or wild-type HRAS, 3-dimensional skin models, skin samples from RASopathy mouse models and patient-derived induced pluripotent stem cells differentiated in keratinocytes. We will apply both single protein analyses (e.g. recombinant protein assays, cell sorting) as well as proteomics technologies (mass spectrometry, kinome profiling). By defining novel dysregulated cellular pathways and mechanisms we expect to uncover alternative treatment strategies which should result in improved management of RASopathies.
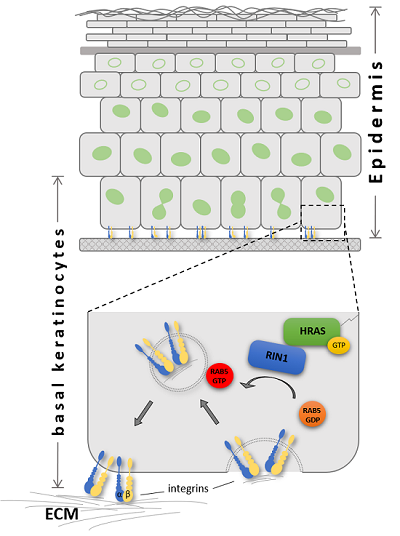
Pathogenic HRAS mutations and dysregulated receptor trafficking. The epidermis is composed of four stratified keratinocyte layers that undergo programmed differentiation. The basal keratinocytes stay in contact with the extracellular matrix (ECM) and the dermis via integrin-based adhesions and hemidesmosomes. The consecutive stratification process requires continuous adaption of contact proteins in epidermal cells. In this context, vesicle-based trafficking is crucial for the turnover of cell contact proteins. Costello syndrome-associated HRAS mutants affect RIN1-RAB5 mediated vesicle-based trafficking of integrins and, thus, epidermal homeostasis.
Major goals:
Based on our results from the previous funding period the primary goals of this project are to uncover the pathomechanisms underlying the cutaneous manifestations in mosaic and non-mosaic RASopathies and to study the pathophysiological basis for mutation-specific phenotypes. In detail, we will study …
- … the function of HRAS-RIN1 signalling in vesicle-based trafficking of membrane proteins and in cytoskeletal dynamics.
- … the pathophysiological relevance of disturbed endosomal sorting in RASopathies in order to uncover biomarkers for RASopathies.
- … the pathophysiological basis for mutation-specific phenotypes.
Publications:
- Gripp KW, Kolbe V, Brandenstein LI, Rosenberger G. Attenuated phenotype of Costello syndrome and early death in a patient with an HRAS mutation (c.179G>T; p.Gly60Val) affecting signalling dynamics. Clin Genet 2017;92:332-7. PMID: 28139825
- zum Büschenfelde UM, Brandenstein LI, von Elsner L, Flato K, Holling T, Zenker M, Rosenberger G, Kutsche K. RIT1 controls actin dynamics via complex formation with RAC1/CDC42 and PAK1. PLOS Genet; 2018 May 7;14(5):e1007370. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1007370. (Consortium joint publication). PMID: 29734338
TP6 project description - previous funding period FP1








